Introduction to Ruby
Ruby is a pure Object-Oriented language developed by Yukihiro Matsumoto (also known as Matz in the Ruby community) in the mid 1990’s in Japan. Everything in Ruby is an object except the blocks but there are replacements too for it i.e procs and lambda. The objective of Ruby’s development was to make it act as a sensible buffer between human programmers and the underlying computing machinery. Ruby has similar syntax to that of many programming languages like C and Java, so it is easy for Java and C programmers to learn. It supports mostly all the platforms like Windows, Mac, Linux.
Ruby is based on many other languages like Perl, Lisp, Smalltalk, Eiffel and Ada. It is an interpreted scripting language which means most of its implementations execute instructions directly and freely, without previously compiling a program into machine-language instructions. Ruby programmers also have access to the powerful RubyGems (RubyGems provides a standard format for Ruby programs and libraries).
Beginning with Ruby programming:
1. Finding a Compiler:
Before starting programming in Ruby, a compiler is needed to compile and run our programs. There are many online compilers that can be used to start Ruby without installing a compiler:
https://www.jdoodle.com/execute-ruby-online
There are many compilers available freely for compilation of Ruby programs.
2. Programming in Ruby:
To program in Ruby is easy to learn because of its similar syntax to already widely used languages.
Writing program in Ruby:
Programs can be written in Ruby in any of the widely used text editors like Notepad++, gedit etc. After writing the programs save the file with the extension .rb
Let’s see some basic points of programming:
Comments: To add single line comments in Ruby Program, # (hash) is used.
Syntax:
# Comment
To add multi-line comments in Ruby, a block of =begin and =end (reserved key words of Ruby) are used.
Syntax:
=begin
Statement 1
Statement 2
...
Statement n
=end
Example:
A simple program to print “Hello Geeks!! Welcome to GeeksforGeeks”
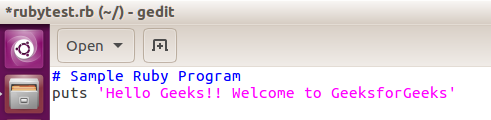
Output:
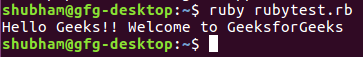
Note: In the output screen, it can be seen how a program is made to run on prompt.
Explanation: First line consist of single line comment with “#” as prefix. Second line consist of the message to printed and puts is used to print the message on the screen.
As everything has some advantages and disadvantages, Ruby also has some advantages along with some disadvantages.
Advantages of Ruby:
- The code written in Ruby is small, elegant and powerful as it has fewer number of lines of code.
- Ruby allows simple and fast creation of Web application which results in less hard work.
- As Ruby is free of charge that is Ruby is free to copy, use, modify, it allow programmers to make necessary changes as and when required.
- Ruby is a dynamic programming language due to which there is no tough rules on how to built in features and it is very close to spoken languages.
Disadvantages of Ruby:
- Ruby is fairly new and has its own unique coding language which makes it difficult for the programmers to code in it right away but after some practice its easy to use. Many programmers prefer to stick to what they already know and can develop.
- The code written in Ruby is harder to debug, since most of the time it generates at runtime, so it becomes difficult to read while debugging.
- Ruby does not have a plenty of informational resources as compared to other programming languages.
- Ruby is an interpreted scripting language, the scripting languages are usually slower than compiled languages therefore, Ruby is slower than many other languages.
Applications:
- Ruby is used to create web applications of different sorts. It is one of the hot technology at present to create web applications.
- Ruby offers a great feature called Ruby on Rails (RoR). It is a web framework that is used by programmers to speed up the development process and save time.